Android 14 Compatibility Guide
With the continuous evolution of mobile operating systems, Google Play has introduced new requirements for the app’s targetSdkVersion.
Starting from August 31, 2024, new apps and app updates must target Android 14 (API level 34) or higher to be submitted to Google Play.
If more time is needed to update the app, an extension can be requested until November 1, 2024.If necessary, check the Google Play Console extension form, which is generally available in the Inbox on the app management page.
For more details, see Requirements for Apps on Google Play for Target API Level.
This document is intended for developers who wish to upgrade their project’s targetSdkVersion to 34. It provides an overview of the changes and impacts in API level 34, along with methods to identify affected areas and modification strategies. This will help ensure your app delivers a good experience on Android 14.
To avoid compilation errors, both compileSdkVersion and targetSdkVersion must be upgraded to 34.
Android 14 Behavioral Change Impact Points
The following lists features and behavior changes that may affect game developers. For all changes in Android 14, please refer to: https://developer.android.com/about/versions/14/summary
Restrictions on implicit and pending intents
For apps with targetSdkVersion=34, implicit intents have the following restrictions on Android 14:
- Implicit intents can only be delivered to exported components.Apps must use explicit intents to deliver to non-exported components, or mark the component as exported.
- If an app creates a mutable
PendingIntentusing an intent without a specified component or package, the system will throw an exception.
Troubleshooting Method
Developers can unpack the APK build (see Appendix) and check the AndroidManifest to see if it contains components that meet the following conditions:
- Android component declaration has the attribute
android:exported="false" - Android component declaration includes an
intent-filterwith a custom action
If there are component declarations that meet the above conditions, implicit intent-based component launches may occur. In that case, please contact [diemliang (梁世宇)] for further investigation.
Sample Code:
<service android:name="com.example.ExampleService"
android:exported="false">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.EXAMPLE_ACTION"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
</intent-filter>
</service>
Runtime-Registered Broadcast Receivers Must Specify Exported Flag
Broadcast receivers are commonly used to listen for device state changes, such as network connectivity switches or battery level changes, and are a frequently used feature.
For apps with targetSdkVersion=34, BroadcastReceiver instances registered at runtime via Context must have their exported attribute specified in the parameters, otherwise an exception will be thrown.
Troubleshooting Method
The business team can [unpack the APK build] (#Appendix) and search the smali files for the following key code:
Landroid/content/Context;->registerReceiver(Landroid/content/BroadcastReceiver;Landroid/content/IntentFilter;)Landroid/content/Intent;
If found, it indicates that the logic involves registering a BroadcastReceiver using Context. In that case, please contact [diemliang (梁世宇)] and provide the smali files for further investigation.
For projects using Unity 2020 and earlier, refer to Unity.
Zip Path Validation
For apps with targetSdkVersion=34, if a zip entry name contains “..” or starts with “/”, ZipFile(String) and ZipInputStream.getNextEntry() will throw a ZipException.
This measure is to prevent zip path traversal vulnerabilities.
Troubleshooting Method
The business team can unpack the APK build and search the smali files for the following key code:
Ljava/util/zip/ZipFile;-><init>(Ljava/lang/String;)V
Ljava/util/zip/ZipInputStream;->getNextEntry()Ljava/util/zip/ZipEntry;
If found, it indicates that the business logic involves using ZipFile or ZipInputStream, and it is necessary to verify whether the functionality using these interfaces works correctly on Android 14.
For zip files extracted using the above interfaces, if the paths of the compressed files contain “..” or start with “/”, it is recommended to modify the structure of the zip file and the extraction method.In that case, please contact [diemliang (梁世宇)] for further investigation.
User consent must be obtained for every MediaProjection capture session
For apps with targetSdkVersion=34, your app must obtain user consent before each Capture Session.Each Capture Session can only involve a single call to MediaProjection#createVirtualDisplay, and each MediaProjection instance can only be used once.
This API is related to screen recording and is commonly used for capturing players’ highlights.
Troubleshooting Method
The business team can unpack the APK build and search the smali files for the following key code:
Landroid/media/projection/MediaProjection;->createVirtualDisplay(
Landroid/media/projection/MediaProjectionManager;->createScreenCaptureIntent()
If found, it indicates that the business logic involves using MediaProjection, and it is necessary to verify whether the functionality using this interface works correctly on Android 14, with particular attention to scenarios where the interface is invoked multiple times within a single session.In that case, please contact [diemliang (梁世宇)] for further investigation.
Foreground Services Must Specify Types
When opening Google login or WebView content in the game, the game process may enter the background and potentially be killed by the system.To prevent this issue, you can grant foreground service permissions to the game.
For apps with targetSdkVersion=34 that use foreground services, each foreground service must specify at least one foreground service type.You should choose a foreground service type that best represents your app’s use case.The system requires specific types of foreground services to satisfy particular use cases.
You also need to submit a foreground service declaration in Google Play Console under App Content > Foreground Service Permissions.For example, if your app uses WebView functionality, select Other, then add a brief description and a video URL showing how the app opens WebView in the game.
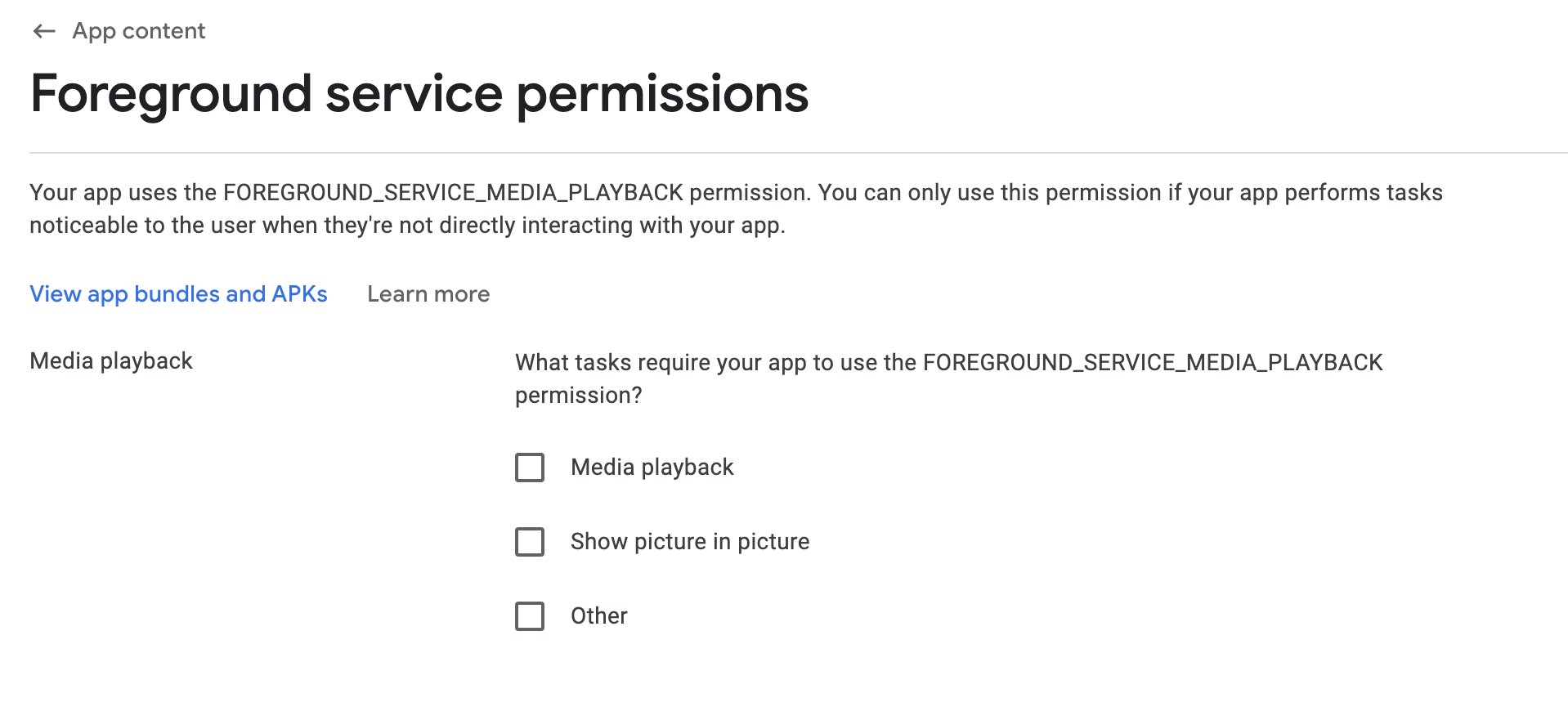
For selectable foreground service types, see Foreground service types are required.
Troubleshooting Method
The business team can unpack the APK build and search the smali files for the following key code to determine whether foreground services are being used:
->startForeground(ILandroid/app/Notification;)V
->startForeground(ILandroid/app/Notification;I)V
If found, you need to check the corresponding Service definition in AndroidManifest.xml to ensure it includes the android:foregroundServiceType attribute and that the type is appropriate.Please contact [diemliang(Liang Shiyu)] for further investigation.
Sample Code:
{/* AndroidManifest.xml */}
<manifest ...>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE" />
{/* Add the corresponding specific permission; in this example, the permission corresponding to mediaPlayback: FOREGROUND_SERVICE_MEDIA_PLAYBACK */}
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_MEDIA_PLAYBACK" />
<application ...>
{/* Define foregroundServiceType in the service */}
<service
android:name=".MyMediaPlaybackService"
android:foregroundServiceType="mediaPlayback"
android:exported="false">
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
Method to Remove Foreground Service Permissions
- Unity
- Unreal Engine
Add xmlns:tools and the <uses-permission> declaration under the <manifest> node in <ProjectDir>/Assets/Plugins/Android/AndroidManifest.xml:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
package="com.intlgame.demo">
...
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_MEDIA_PLAYBACK" tools:node="remove" />
Add the xmlns:tools and <uses-permission> declarations under the <root> node in <ProjectDir>/Source/<ProjectName><ProjectName>_UPL_Android.xml:
<root xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<addElements tag="manifest">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_MEDIA_PLAYBACK" tools:node="remove" />
</addElements>
The statement tools:node="remove" will remove the permission.
Development Environment Adaptation Changes
- Unity
- Unreal Engine
In Unity 2020 and earlier, UnityPlayerActivity#onCreate uses the registerReceiver method without specifying the exported flag. This causes Unity 2020 and earlier versions to fail on Android 14 when attempting to upgrade targetSdkVersion to 34.
It is recommended to upgrade Unity to an LTS version that fixes this issue or later:
- 2021.3.33f1
- 2022.3.13f1
- 2023.1.20f1
- 2023.3.0a11
For more details, see this Issue report submitted on the Unity Issue Tracker.

Set the game to target Android API level 34 by upgrading the targetSdkVersion in Unreal Engine:
- In your Unreal Engine project, locate the Config folder and open the
DefaultEngine.inifile; - In the
DefaultEngine.inifile, add or modify the following lines to set thetargetSdkVersion:
TargetSDKVersion=34
SDKAPILevelOverride=android-34
- Once the modification is complete, save and close the
DefaultEngine.inifile.
Upgrade Android Gradle Plugin (AGP)
- Unity
- Unreal Engine
According to Google's official documentation Minimum tool versions required for specific Android API levels, when the application targetSdkVersion=34, the minimum AGP version required is 8.1.1.
However, based on actual testing, using 7.1.2 is sufficient to meet the current build requirements, and there is no need to upgrade to the much higher 8.1.1.
- For Unity 2022.2 and above, no action is needed because the default AGP version already meets the requirement
- For Unity versions below 2022.2, follow the steps below to upgrade AGP
Upgrade the Gradle Wrapper version
-
In the Editor menu Unity > Settings > External Tools, locate the Gradle installed with Unity option and uncheck it. Then, in the Gradle path field below, select the path to gradle-7.2-bin on your machine, for example:

-
Modify the environment variables and set the
GRADLE_HOMEvariable to the path of Gradle version 7.2:# sh
export GRADLE_HOME=/Users/***/.gradle/wrapper/dists/gradle-7.2-bin/****/gradle-7.2
export PATH=${PATH}:${GRADLE_HOME}/bin
Modify the AGP version dependency
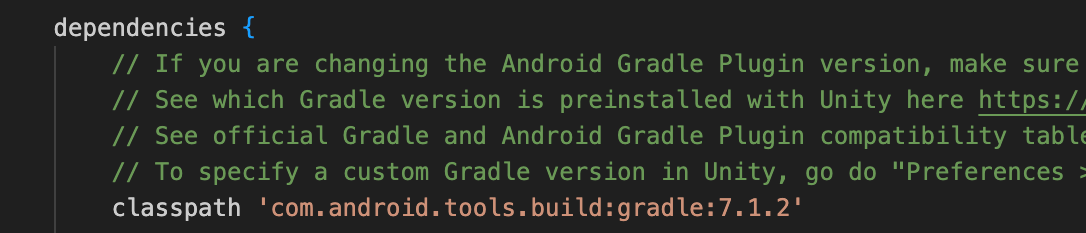
After upgrading to Player Network SDK V1.24, Assets/Plugins/Android/baseProjectTemplate.gradle has already updated AGP to version 7.1.2, so no changes are required.
Check the "com.android.tools.build:gradle:x.x.x" entry in the Assets/Plugins/Android/baseProjectTemplate.gradle file.
If the version is lower than 7.1.2, update it to 7.1.2.Otherwise, no modification is needed.
According to Google's official documentation, Minimum tool versions required for specific Android API levels, when the application uses targetSdkVersion=34, the minimum required AGP version is 8.1.1.
However, based on actual testing, using 7.1.2 is sufficient to meet the current build requirements, and there is no need to upgrade to the much higher 8.1.1.
Follow the steps below to upgrade AGP:
Upgrade the Gradle Wrapper version
-
Download gradle-7.2-bin.zip and extract it;
-
Modify the environment variables and set the
GRADLE_HOMEvariable to the extracted path of gradle-7.2-bin:# sh
export GRADLE_HOME=/Users/***/.gradle/wrapper/dists/gradle-7.2-bin/****/gradle-7.2
export PATH=${PATH}:${GRADLE_HOME}/bin -
Modify the file
/Engine/Build/Android/Java/gradle/gradle/wrapper/gradle-wrapper.properties, and changedistributionUrlto the URL for Gradle 7.2:distributionUrl=https\://services.gradle.org/distributions/gradle-7.2-all.zip
Modify the AGP version dependency
After upgrading to Player Network SDK V1.24, AGP has already been upgraded to version 7.1.2 in INTLSDK/Source/INTLCore/Libs/Android/INTLCore_APL.xml, so no changes are required.
Add or modify the following in the APL file:
<buildscriptGradleAdditions>
<insert>
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:7.1.2'
}
</insert>
</buildscriptGradleAdditions>
Upgrade Java Version
- Unity
- Unreal Engine
When upgrading targetSdkVersion to 34, the Java version also needs to be upgraded:
- For Unity 2022.3 and above, no action is needed because the default Java version already meets the requirement
- For Unity versions below 2022.3, follow the steps below to upgrade Java
-
In
Assets/Plugins/Android/gradleTemplate.properties, addorg.gradle.java.homewith the value set to the path of Java 11, for example:org.gradle.java.home=/Users/***/Library/Java/jdk-11.0.22.jdk/Contents/Home -
Modify the environment variable and set
JAVA_HOMEto the path of Java 11:# sh
# set JAVA_HOME to your jdk 11 installation path.
export JAVA_HOME=/Users/***/Library/Java/jdk-11.0.22.jdk/Contents/Home
export PATH=${PATH}:${JAVA_HOME}/bin
AGP 7.1.2 requires Java 11. If the current Java version is lower than 11, you need to download and install JDK 11 and update the environment variable accordingly:
# sh
# set JAVA_HOME to your jdk 11 installation path.
export JAVA_HOME=/Users/***/Library/Java/jdk-11.0.22.jdk/Contents/Home
export PATH=${PATH}:${JAVA_HOME}/bin
How to verify
Basic Information Confirmation
Unpack the APK, and in the AndroidManifest.xml file inside the package, check the following fields to ensure they meet expectations:
-
Check the
packageattribute in the<manifest>to confirm that the package name is correct; -
Check the
platformBuildVersionCodeattribute in the<manifest>, the expected value should be 34; -
Check the
android:minSdkVersionattribute in the<uses-sdk>, the value should correspond to the minimum Android API level supported by your project;Android API to Android version reference table: https://apilevels.com/
-
Check the
android:targetSdkVersionattribute in<uses-sdk>, the expected value should be 34;
AndroidManifest.xml example:
{/* -AndroidManifest */}
<manifest
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0"
android:compileSdkVersion="34"
android:compileSdkVersionCodename="14"
package="your.package.name"
platformBuildVersionCode="34"
platformBuildVersionName="14">
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="16"
android:targetSdkVersion="34" />
......
Compatibility Testing
Use the produced APK to perform compatibility testing, focusing on its behavior on Android 14 devices, especially scenarios related to the Android 14 behavior changes described in Section 2;
Appendix
APK Unpacking Guide
When verifying whether the game involves any changed APIs, it is recommended to unpack the APK for a global search.The recommended unpacking tool is apktool:
Example usage of apktool:
apktool d your_apk_path.apk
After executing the above command, the unpacked result will be in the /your_apk_path directory:

FAQs
If you encounter problems during the adaptation process, please refer to Android FAQs.
